What factors drive Bitcoin's price?
Touted as “digital gold”, Bitcoin remains volatile and susceptible to macro and internal factors. This currency without a state may seesaw on Fed policy updates, geopolitical tensions, and blockchain industry developments. Our guide outlines the key drivers shaping the BTC price in 2024.
Origins of "digital gold"
The Bitcoin blockchain — the brainchild of the enigmatic Satoshi Nakamoto — went live on January 3, 2009. The beginnings were humble, but the goal was ambitious. Nakamoto intended to launch a "peer-to-peer version of electronic cash" for the world.
Like other proof-of-work blockchains, Bitcoin issues new coins as mining rewards — incentives for network participants that verify blocks of new transactions. As a result of quadrennial halvings, the size of those rewards has shrunk from 50 BTC to 3.125 BTC, supporting the price of the digital asset through a scarcity mechanism.
Dissecting Bitcoin market drivers
The laws of supply and demand are fundamental to TradFi markets. Consumer goods, fiat currencies, and commodities traded spot, from coffee to corn, depend on this correlation.
Prices decline if there is surplus production but the demand fails to keep up. Shrinking supply, on the other hand, tends to bolster value in similar conditions. The same holds for the pioneering cryptocurrency and all its successors.
Past and present of BTC market
Originally, BTC did not have any set monetary value in fiat as there was no dedicated marketplace. The Bitcoin Pizza Day, celebrated on May 22, commemorates the first real-world BTC transaction.
In 2010, a Bitcointalk.com forum user exchanged 10,000 coins for two pizzas (equivalent to $40 at the time or $600 million at press time). As others started selling goods and services for BTC, the market formed and grew, supporting price discovery.
Supply, demand, and free-market pricing
The free market still determines Bitcoin's valuation, with holders buying everything from luxury items to real estate, and corporate giants like MicroStrategy accumulating significant stockpiles. Price discovery primarily happens on centralized crypto exchanges (CEXs), where users trade Bitcoin for fiat currencies and other crypto tokens.
When demand outpaced supply, the price surged. BTC surpassed $10,000 in July 2020, reached nearly $70k in November 2021, and then rocketed to $73,738.00 — the current all-time high — on March 14, 2024.
The supply of the pioneer is limited to 21 million, expected to be mined by 2140. Only a predetermined amount of bitcoins may be created every year based on the block reward size.
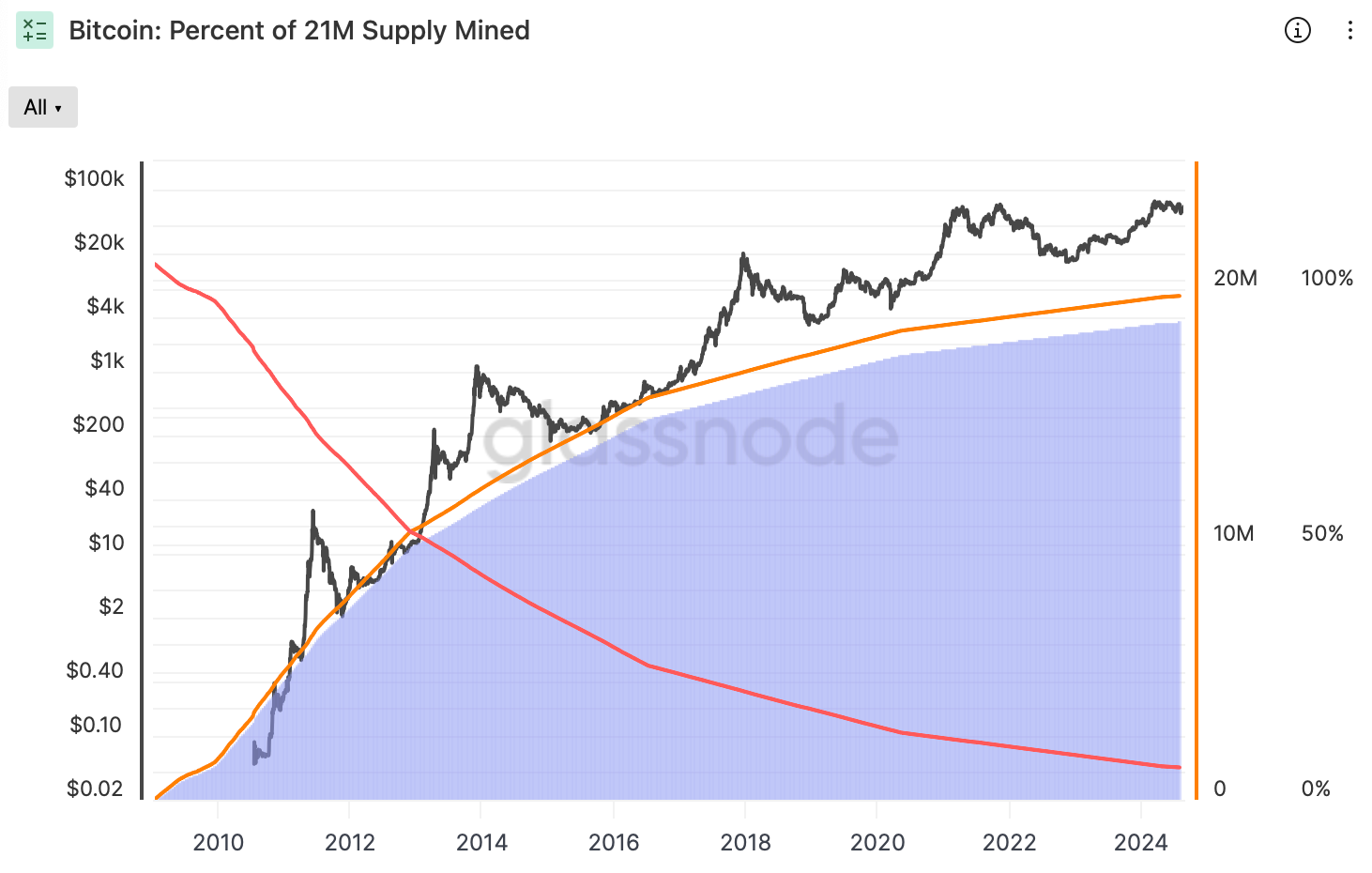
The pace of issuance slows down, causing a supply contraction. The latest halving event in April 2024 slashed it to 3.125 BTC per block, eating into miners’ profits and causing the smallest ones to shut down. Hence, the dwindling of the BTC supply is not merely regular. It is also public knowledge, ensuring transparency that adds to the demand.
Besides supply and demand, Bitcoin is susceptible to media narratives, regulatory changes, and political announcements. The cost of mining may also affect its price, although the relationship is debated. However, the market behavior of large miners — significant sales of holdings — exerts negative pressure, like whale selling in general.
What drives demand for BTC?
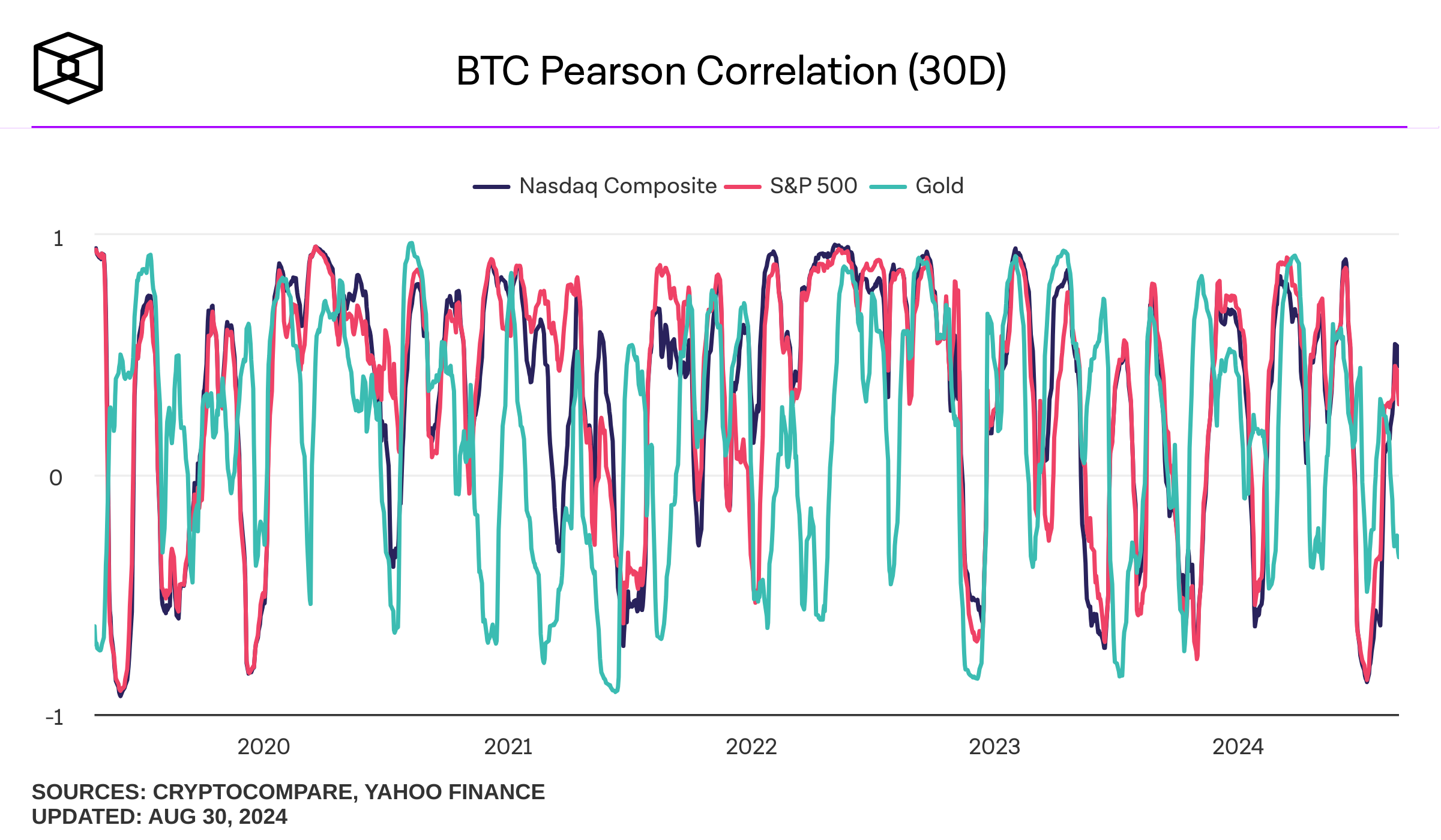
Unlike Ethereum, which powers a plethora of decentralized applications, staking, yield farming, and other earning avenues, Bitcoin is primarily a store of value. It is perceived as digital gold and a hedge against inflation, as it does not closely follow stocks.
As of August 30, 2024, Bitcoin's 30-day Pearson correlation to the S&P 500 is at 0.29, as opposed to 0.48 for the Nasdaq. Values between 0 and 1 indicate a positive linear correlation, with 1 corresponding to a perfect positive relationship.
BTC is more than an alternative to fiat currency or payment systems. Thanks to its limited supply in decentralized nature, it works differently from national currencies and TradFi instruments. However, it still depends on the same macro factors (more on this below).
One of the most appealing characteristics of Bitcoin is its resistance to confiscation and censorship. Bitcoin users can conduct peer-to-peer transactions without needing a trusted third party, with an enhanced sense of security and confidence.
Impact of crypto regulations
Crypto regulation varies significantly around the world. The European Union has recently introduced the Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation, its first comprehensive framework for crypto focused on financial stability and consumer protections
In the United States, Bitcoin is officially a commodity; the CTFC classified it under the US Commodity Exchange Act (CEA) in 2015. The SEC Chairman, Gary Gensler, further confirmed this in 2024, and the launch of spot Bitcoin ETFs underscored Bitcoin's status. Meanwhile, in El Salvador, Bitcoin has been official legal tender since 2021.
The absence of a unified regulatory approach to Bitcoin has its own set of advantages. It allows users to conduct cross-border transfers quickly and at a lower cost compared to traditional finance. As governments may not impose fiat controls, crypto provides unrivaled freedom and flexibility.
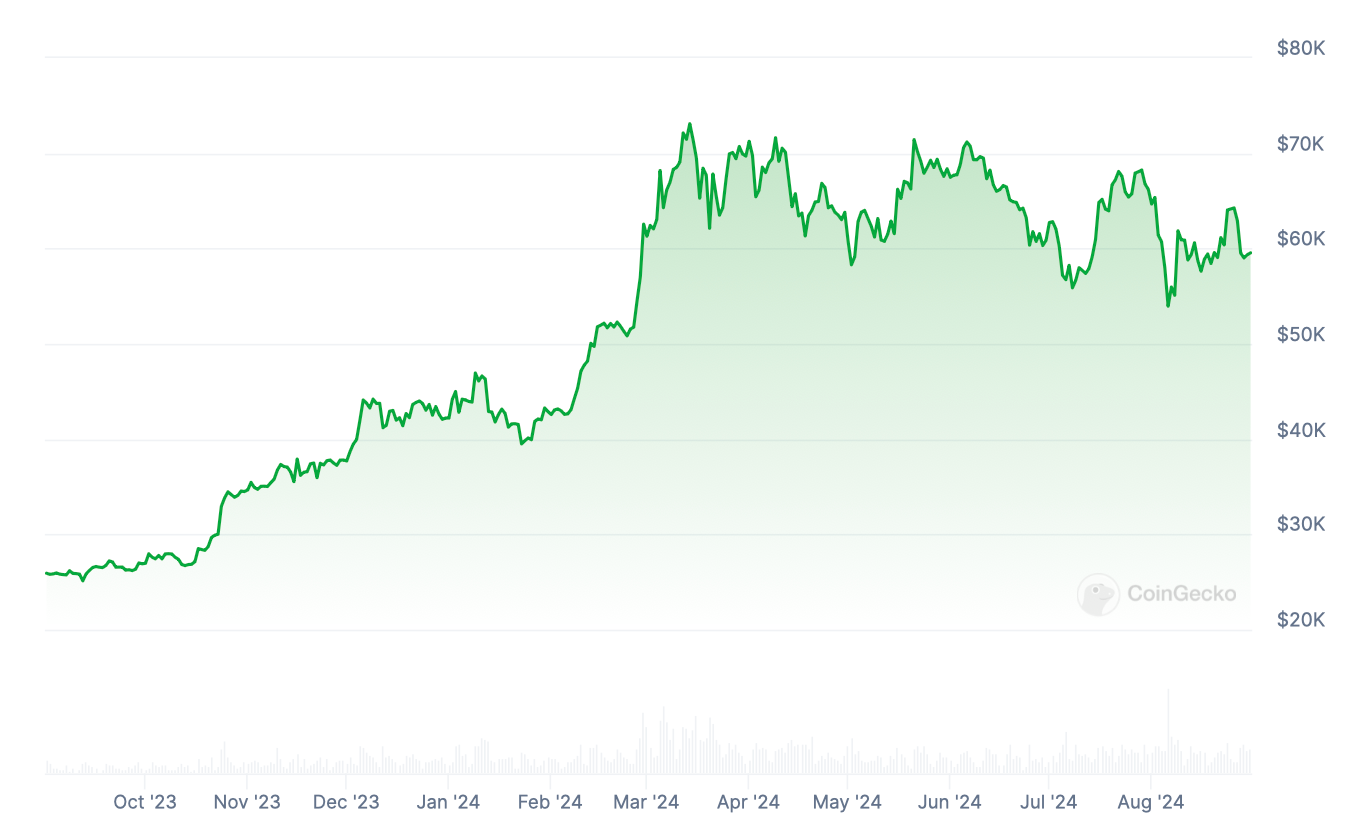
However, Bitcoin remains a volatile asset. In August 2024, its price zigzagged between $50k and $64k, affected by macro drivers, whale activities, and ETF flows, among other things. It remains susceptible to regulatory factors, such as the SEC's approval of spot Bitcoin ETFs in January 2024, which fueled a rally.
Sensitivity to macro drivers
Bitcoin has reacted strongly to the Fed policy decisions and US inflation data after the regulator raised the benchmark interest rate to a 23-year high in 2023. FOMC meetings and Chair Jerome Powell’s speeches move crypto along with other risk assets. As tightening policies lower the interest rates, cryptocurrencies may see their prices fall.
Traders also react to promises, such as Donald Trump's intention to set up a Bitcoin strategic Reserve, announced during his presidential campaign.
Whale BTC transfers
Whales — large BTC holders, high-net-worth individuals, and businesses — can significantly influence Bitcoin's prices, leading to either undervaluation or overvaluation. For instance, in the summer of 2024, the market reacted to substantial transfers by the German and US governments, as well as outflows from the Mt. Gox wallets as part of the exchange's creditor redemptions.
Crypto bans
Government-imposed restrictions on crypto transactions or Bitcoin mining can also have a profound impact. For example, China's blanket ban on trading and transactions in 2021 forced local mining farms to operate underground or relocate abroad, while the BTC price sank from roughly $51k to around $41k in September.
However, it quickly rebounded to higher highs as the operations resumed. At press time, outright bans also exist in Algeria, Bangladesh, Saudi Arabia, Morocco, Nepal, Pakistan, Bolivia, and Tunisia.
Finally, media and social media postings can be a double-edged sword for BTC. Any changes in technical indicators and any of the drivers discussed above can quickly become public knowledge. Positive and negative news alike have the power to swiftly alter market sentiment — and consequently, the BTC price.
Overview of competition
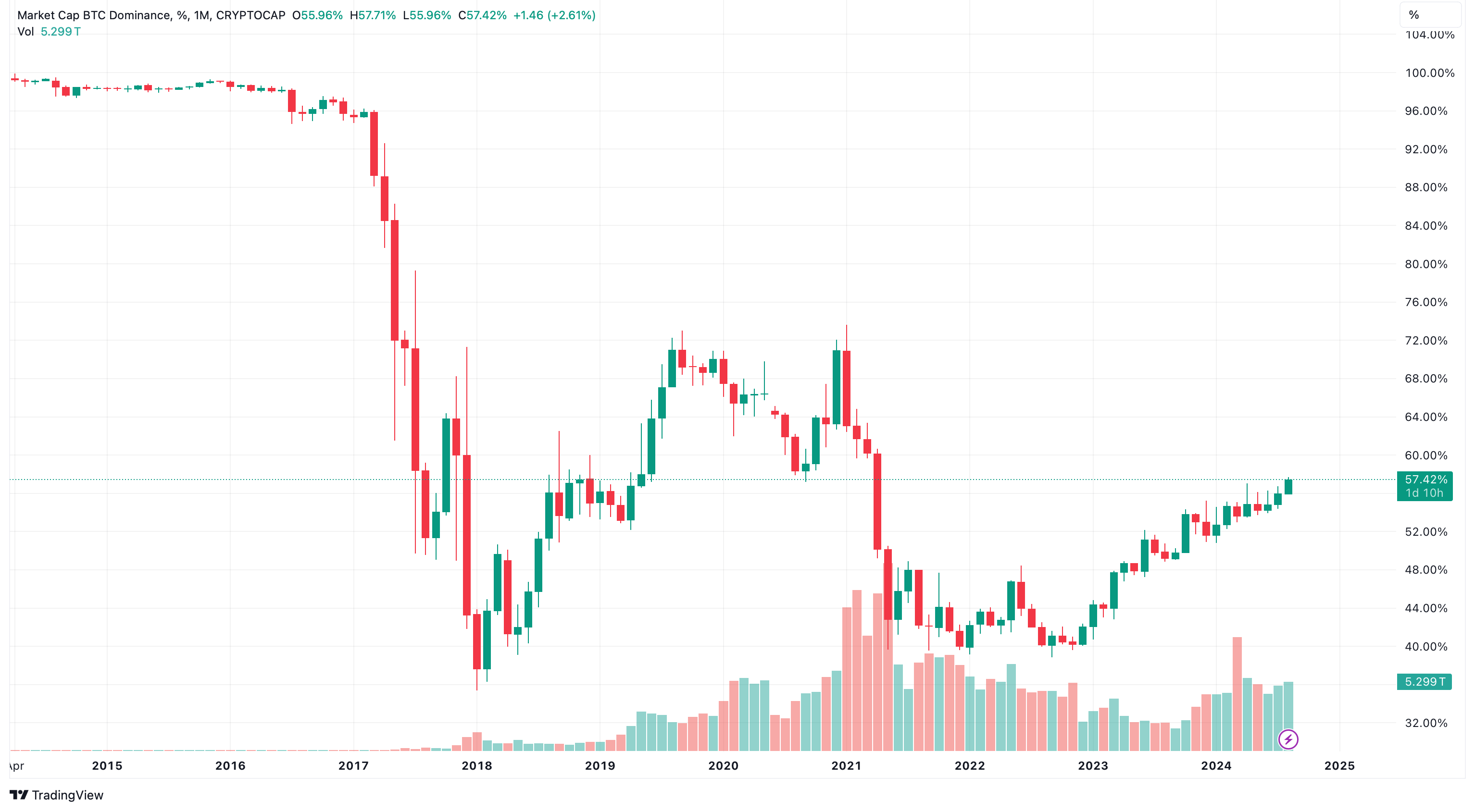
Bitcoin's market cap stands unrivaled at $1.1T; it coexists with hundreds of other cryptocurrencies. As of March 2024, there were over 13,000 tokens in circulation, vying for investment dollars.
The coin's dominance, which accounted for over 80% of the total market cap in 2017, has shrunk to 57% as of August 30, 2024. The growing popularity of alternative coins, or altcoins, is a major reason for the shift.
The DeFi, or decentralized finance boom, is a promising trend that largely depends on the Ethereum network and its ether coin, serving as gas for transactions. Since 2017, the ETH dominance has decreased from 24% to 14.79%, with the number of Layer-2 networks on top of it growing rapidly. This trend and the emergence of new coins and tokens daily are changing the dominance dynamics.
Final words
Although Bitcoin is independent of any company or government, it has grown susceptible to US macro drivers in recent years. Yet its value is primarily defined by the capped supply and scarcity, demand dynamics, competition from other cryptos, and the overall investor sentiment. Contrasting with the potentially unlimited issuance of stocks or fiat currencies, Bitcoin is a unique financial asset perceived as an alternative store of value and "digital gold."



